As an educator, you’re constantly seeking ways to improve student outcomes. Although not new, social-emotional learning (SEL) has gained significant traction in recent years. SEL is a set of universal, transferrable skills vital for activating humans’ innate capacity to form social connections and empathy. SEL supports students in becoming successful, productive adults, both personally and professionally.
As an educator, you’re constantly seeking ways to improve student outcomes. Although not new, social-emotional learning (SEL) has gained significant traction in recent years. SEL is a set of universal, transferrable skills vital for activating humans’ innate capacity to form social connections and empathy. SEL supports students in becoming successful, productive adults, both personally and professionally.
But does SEL really impact academic performance? Let’s explore the compelling evidence.
Defining Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) is how students acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, empathize with others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions. SEL includes five core competencies:
- Self-awareness involves recognizing one’s emotions, thoughts, values, strengths and weaknesses, and self-confidence.
- Self-management refers to being able to control one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors, manage stress and control impulses, and be self-motivated.
- Social awareness is the ability to relate to and empathize with others, including those with different backgrounds. It is also the ability to understand and operate within ethical norms.
- Relationship skills are the ability to create and maintain healthy relationships, including with those from different backgrounds. They also include the ability to communicate with others, listen, cooperate, stand up to negative pressure, and work through conflict productively.
- Responsible decision-making refers to making constructive and healthy choices about personal behavior and social interactions, as well as being aware of and responsive to potential consequences.
The SEL-Academic Success Link
Research consistently shows a strong connection between SEL and academic achievement. Extensive studies, including hundreds of investigations involving over one million students worldwide from PreK to 12th grade, consistently demonstrate that SEL positively impacts students’ academic performance. Students engaged in SEL tend to exhibit better “school functioning,” as evidenced by higher grades, improved test scores, consistent attendance, and more consistent homework completion.
In addition, a concept within the self-awareness competency is growth mindset. Growth mindset is the opposite of a fixed mindset. When students develop a growth mindset they are able to tackle new challenges and persist in the face of setbacks or failures. Students with a growth mindset experience higher academic achievement because their focus shifts from achieving outcomes to improving through effort and valuing the skills developed throughout the learning process. Research shows that students with a growth mindset outperform their peers and learn the equivalent of an additional 33 days of learning in English language arts and 31 days in mathematics within an academic year.
Here are five specific ways SEL contributes to student success:
- Improves Classroom Behavior: Research from Yale School of Medicine shows that students with strong social-emotional skills can better focus on learning, leading to fewer disruptions and more productive class time.
- Enhances Problem-Solving Abilities: SEL equips students with critical thinking skills that directly apply to academic challenges.
- Increases Motivation and Persistence: Students who manage their emotions are more likely to persevere through academic difficulties.
- Develops Better Stress Management: Reduced stress improves cognitive function and learning capacity.
- Builds Stronger Student-Teacher Relationships: Positive relationships foster a supportive learning environment, enhancing student engagement.
How To Integrate SEL into the Curriculum
Integrating SEL into the curriculum is not something that requires a huge lift on teachers, it is about simply tweaking daily practice to be more intentional in providing safe spaces for students to practice the essential SEL skills. Here are some strategies educators can employ:
- Incorporate SEL into Daily Activities: Incorporating SEL into your daily classroom routine provides students with regular opportunities to practice essential life skills. Consider starting the day with morning meetings where students can share their feelings, set personal goals, or engage in mindfulness exercises. Reflective journaling is another effective strategy; it allows students to write about their emotions, experiences, or reactions to different situations.
These practices foster self-awareness, emotional regulation, and empathy, creating a supportive environment where students feel comfortable exploring and expressing their feelings. - Use SEL-Focused Literature: Integrating books and stories emphasizing SEL themes into your language arts curriculum greatly enhances SEL instruction. Choose literature that delves into emotions, relationships, and personal challenges, providing relatable scenarios for students.
Lead discussions that encourage students to examine characters’ emotional responses, decision-making processes, and interpersonal interactions. It strengthens literacy skills and deepens students’ comprehension of SEL concepts, helping them connect these ideas to their lives. - Model SEL Competencies: As educators, your behavior sets a powerful example for your students. In daily interactions, demonstrate empathy, active listening, conflict resolution, and emotional regulation to model SEL competencies. Showing patience, understanding, and respect provides a tangible example of navigating social and emotional situations.
These real-life demonstrations of SEL skills reinforce classroom teachings and inspire students to adopt these behaviors, fostering a positive and empathetic classroom culture.
Empower Student Success with SEL
All 50 states have included SEL skills in their educational standards for pre-K students. Additionally, 27 states have expanded these SEL skills to encompass pre-K through 12th-grade students. The rest of the states mainly concentrate their SEL standards on younger students. The evidence is clear: SEL is not just a “nice-to-have” but a critical component of student success. By prioritizing SEL, educators can help students develop the skills necessary for academic achievement and lifelong success.
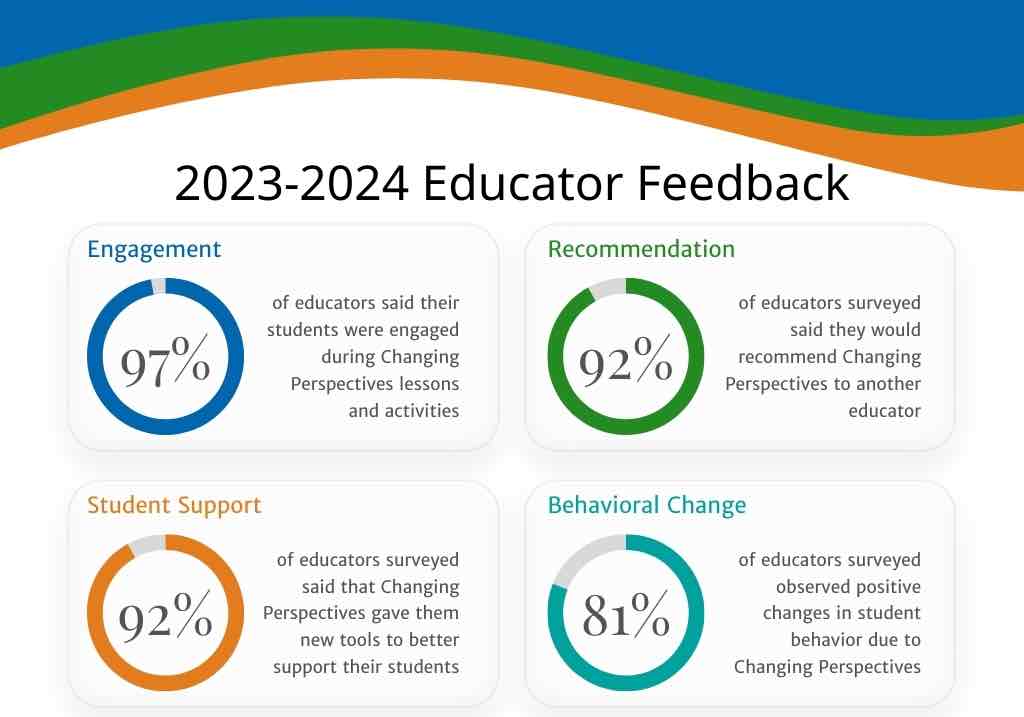
Discover how the Changing Perspectives curriculum resources can integrate SEL into your classroom, youth programs, and after-school activities. Teachers who have worked with us have noted positive changes in academic achievement, student engagement, and behavior as a result of consistent implementation of SEL curriculum resources. Schedule a complimentary consultation to learn how our curriculum can transform your educational environment!