Before the outbreak of COVID-19, the mental health of K-12 students was already a growing concern. However, the pandemic has worsened this mental health crisis even further. Lockdowns, extended periods of virtual learning, social isolation, and the impact of the virus on family members have all taken a significant toll on our children’s health and well-being. Due to school closures and social distancing, many students did not receive the needed support. Even now, there are no signs of improvement, and the mental health of our children and youth remains a pressing issue.
Before the outbreak of COVID-19, the mental health of K-12 students was already a growing concern. However, the pandemic has worsened this mental health crisis even further. Lockdowns, extended periods of virtual learning, social isolation, and the impact of the virus on family members have all taken a significant toll on our children’s health and well-being. Due to school closures and social distancing, many students did not receive the needed support. Even now, there are no signs of improvement, and the mental health of our children and youth remains a pressing issue.
According to a survey conducted during the 2022-23 school year, almost half of all students reported that depression, stress, or anxiety interferes with their academic performance. This percentage has steadily increased since the pandemic’s beginning, with a noticeable rise from 39% in the spring of 2020 to 48% in the 2022-23 school year. Additionally, only 41% of students believed they had a reliable adult at school to talk to when feeling upset, stressed, or facing any issues, which is a decline from the pre-COVID-19 figure of 46%.
Supporting Student Mental Health in Schools
Prioritizing mental health in schools is crucial to creating a culture of well-being and monitoring mental health issues among students. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), promoting social-emotional learning (SEL) is an effective strategy for achieving this. Social-emotional learning equips students with the essential tools to manage their emotions, foster social-emotional development, improve their well-being, and develop the following skills:
- empathy
- communication skills
- social skills
- emotional competence
- positive relationships with peers
- emotional intelligence
- coping strategies and problem-solving skills
These skills are critical for students’ success and well-being inside and outside the classroom. They help students navigate challenges and handle difficult situations effectively, preparing them for the complexities of life. They also enable students to better understand and address real-world issues, such as poverty, race and gender inequality, and social justice, which can significantly impact their mental health.
Implementing SEL in Schools
Social-emotional learning is not a standalone subject but rather an integrated, holistic approach that prioritizes student well-being. When integrated into all aspects of school life, it positively impacts student mental health and contributes to an improved school environment. To create a positive learning environment that supports the mental health of students by implementing social-emotional learning, school leaders and educators should:
- Create a safe and inclusive learning environment.
- Encourage open communication and positive relationships.
- Prioritize resources that help develop social and emotional skills.
- Provide tools to manage stress and anxiety.
- Incorporate activities that promote mental and emotional well-being.
- Teach students about self-care and seeking help when needed.
- Monitor well-being and intervene if necessary.
- Advocate for a culture of kindness, empathy, and belonging.
- Provide ongoing support for educators through training and development.
- Collaborate with families to reinforce social-emotional skills.
SEL Activities to Support Emotional Well-Being
Supporting young people’s mental health starts with them understanding and being in tune with their emotions. Social and emotional learning helps students better understand and regulate their emotions, express themselves healthily, and build positive relationships with their peers and teachers. Educators can help students develop these essential life skills within a relevant context by embedding SEL interventions into the existing curriculum.
Here are some ideas to engage with your students.
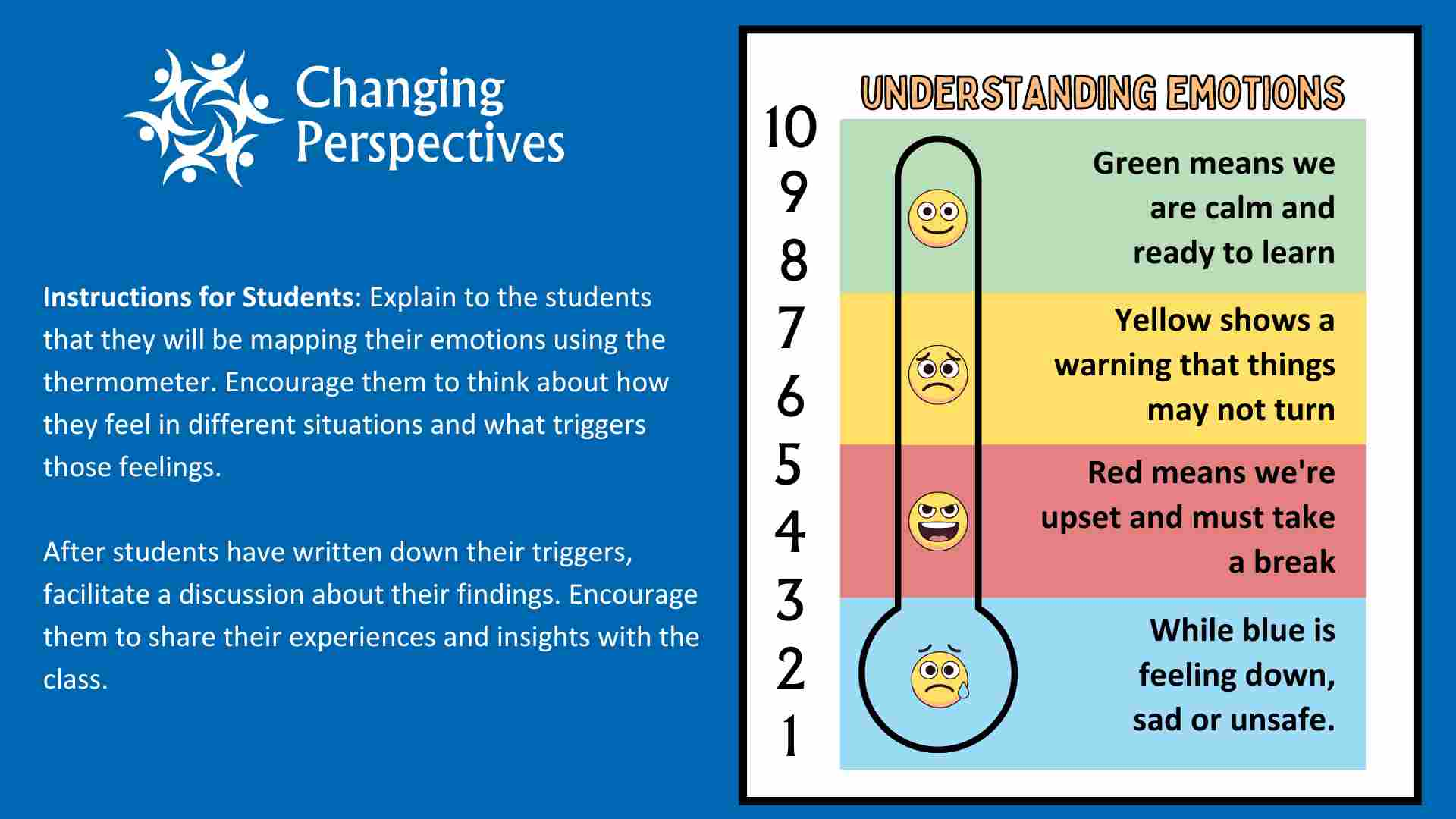
Feelings Thermometer Exercise
This exercise aims to increase students’ emotional awareness and build their life skills to proactively address their mental health needs. To complete this task, you will require materials such as paper or a whiteboard, markers, and a list of emotions.
- Prepare the Thermometer: Draw a large thermometer shape on the paper or whiteboard. Label the left-hand side with numbers, starting from 1 at the bottom and increasing upwards. Leave space next to each number for writing.
- Label the Emotions: Write different emotions along the thermometer, starting with “calm” at the bottom and “very upset” at the top. Ensure there’s enough space between each emotion for writing.
- Instructions for Students: Explain to the students that they will be mapping their emotions on the thermometer. Encourage them to think about their feelings and what triggers them in different situations.
- Guidance for Identifying Triggers: Guide students to think about what makes them feel each emotion. For example, for “calm,” they might write down activities like reading a book or spending time with a pet. For “very upset,” they might list situations such as arguments with friends or feeling left out.
- Facilitate Discussion: After students have written down their triggers, facilitate a discussion about their findings. Encourage them to share their experiences and insights with the class.
- Reflection and Application: Conclude the activity by encouraging students to reflect on how understanding their triggers can help them manage their emotions better in various situations. Encourage them to apply this knowledge in their daily lives.
Mindfulness Exercises and Practices for the Classroom
Mindfulness exercises can help students manage stress more effectively by improving their understanding of thoughts and emotions. Students can integrate these simple yet effective practices into their daily routines to manage overwhelming emotions and promote a sense of calm and stability.
- Visualization: Have students close their eyes and imagine themselves as a tree with roots extending deep into the earth. Encourage them to feel the stability and support of the earth beneath them.
- Mindful breathing: Guide students to take slow, deep breaths while focusing on the sensation of their breath entering and leaving their body. This can help bring their attention back to the present moment and away from anxious thoughts.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Starting from the top of the head, have students tense and then relax each muscle group in their body one at a time. This can help release physical tension and promote a sense of relaxation.
- Grounding objects: Have students hold onto a small object, such as a rock, crystal, or stress ball, and focus on its texture, weight, and temperature. This can bring their attention back to the present moment and provide comfort.
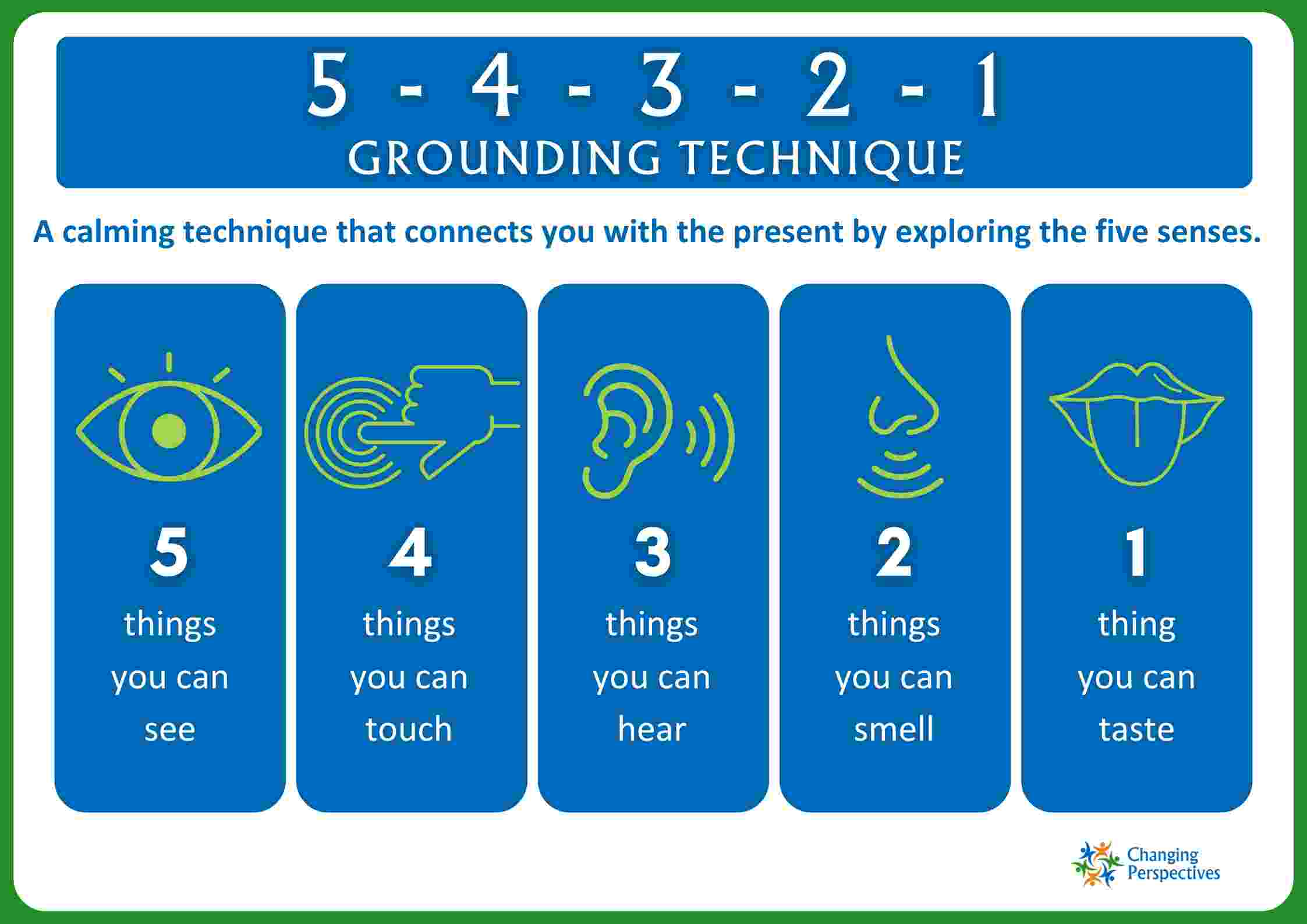
- 5-4-3-2-1 technique: Have students identify five things they can see, four things they can touch, three things they can hear, two things they can smell, and one thing they can taste. This sensory awareness exercise can bring them back to the present moment and increase their sense of grounding.
Positive Self-Talk Practices
Positive self-talk effectively boosts student self-esteem and emotional regulation and helps foster a positive self-image. This skill can be a valuable tool for students to navigate challenging situations and build resilience in adversity. Here are some tips for teaching students how to engage in positive self-talk:
- Start by explaining the concept of self-talk to students and encourage students to pay attention to their self-talk and recognize when they are self-critical or pessimistic.
- Help students identify negative self-talk patterns by journaling or logging their thoughts and feelings throughout the day. Encourage them to notice when they are harsh or critical towards themselves and identify recurring negative thoughts or beliefs.
- Teach students to challenge negative self-talk. Once students have identified their negative self-talk patterns, help them learn how to challenge and reframe these thoughts. Encourage students to ask themselves questions like, “Is this thought true?” or “Is there a more balanced way to view this situation?”
- Encourage students to replace negative self-talk with positive affirmations. Help students develop positive statements or affirmations that they can use to counteract negative self-talk. Encourage students to repeat these affirmations regularly and use them to boost their self-esteem.
- As a teacher, it’s important to model positive self-talk for your students. Be mindful of your self-talk and show students how to respond to challenging situations with words of encouragement and self-compassion. Provide positive reinforcement and feedback when you observe students practicing positive self-talk.
By teaching students how to practice positive self-talk, you can help them develop a healthier relationship with themselves and build their self-confidence.
Additional Resources
Are you interested in discovering more SEL strategies that can help support your students’ mental health and overall well-being?
Our social-emotional learning curriculum is relevant for students of all ages and backgrounds. Designed for educators by educators, our customizable curriculum contains a curated library of learning resources that provide educators with the flexibility and autonomy they need to address the specific needs of their students. Our easy-to-navigate online portal provides access to our curriculum resources anywhere, anytime.