 If you work in education, it’s no surprise that the focus has expanded beyond traditional academic subjects to include the holistic development of individuals. Social-emotional learning (SEL) has emerged as a critical component of education, emphasizing the cultivation of essential life skills beyond textbooks and classrooms. But what is SEL? Let’s dive into SEL’s fundamentals and explore the core principles that form the building blocks for personal growth, resilience, and success.
If you work in education, it’s no surprise that the focus has expanded beyond traditional academic subjects to include the holistic development of individuals. Social-emotional learning (SEL) has emerged as a critical component of education, emphasizing the cultivation of essential life skills beyond textbooks and classrooms. But what is SEL? Let’s dive into SEL’s fundamentals and explore the core principles that form the building blocks for personal growth, resilience, and success.
Definition of Social-Emotional Learning
SEL is a framework for helping students develop the skills to interact with others, manage their emotions and behaviors, and grow into confident, productive, and empathetic individuals. At its core, SEL is organized around five fundamental competencies, each playing a pivotal role in shaping emotionally intelligent and resilient people. It recognizes the interconnectedness of emotions, behavior, and academic performance. Applying SEL equips students with the tools needed to navigate the complexities of life successfully, especially with the impacts of COVID-19. Let’s break it down.
The Five Core Competencies of SEL
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) identifies five core competencies of social and emotional learning (SEL). These competencies are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. Let’s take a closer look at each of them.
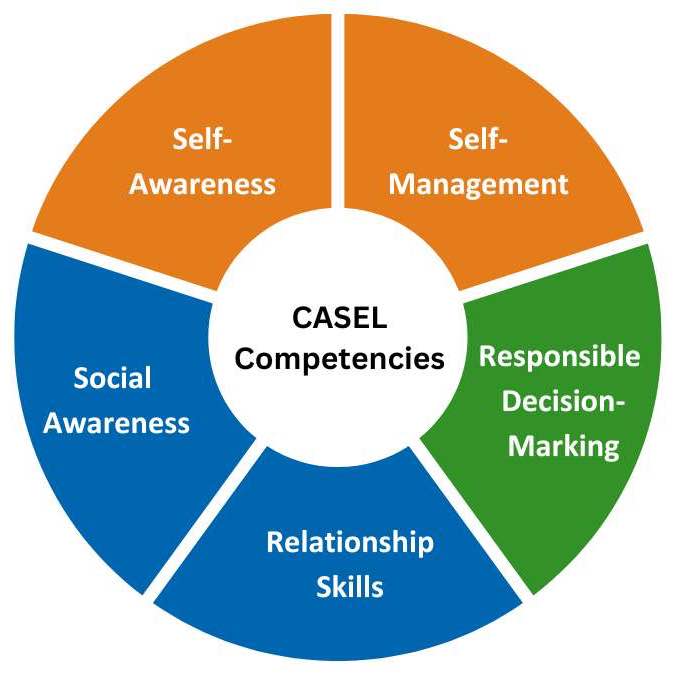 Self-Awareness:The first pillar is self-awareness, the ability to recognize and understand one’s emotions, strengths, and areas for growth. Individuals with solid self-awareness are better equipped to navigate the complexities of life. They can identify how emotions influence their thoughts and actions. Through a growth mindset, they can overcome challenges. The journey of self-discovery sets the stage for a deeper understanding of personal values and aspirations.
Self-Awareness:The first pillar is self-awareness, the ability to recognize and understand one’s emotions, strengths, and areas for growth. Individuals with solid self-awareness are better equipped to navigate the complexities of life. They can identify how emotions influence their thoughts and actions. Through a growth mindset, they can overcome challenges. The journey of self-discovery sets the stage for a deeper understanding of personal values and aspirations.- Self-Management: Building upon self-awareness, self-management is the competency that empowers individuals to regulate their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively. It involves developing strategies for stress management, impulse control, and goal-setting. Children and adults who manage their feelings are better equipped to handle challenging situations. They’re also more likely to adapt and push through challenges without giving up. Self-management fosters emotional well-being, maintains a positive mindset, and takes initiative with regulation.
- Social Awareness: Social awareness extends the focus beyond oneself to an understanding and empathy for others. It involves recognizing and appreciating diverse perspectives, cultures, and backgrounds. Socially aware children are attuned to the emotions and needs of those around them, laying the groundwork for building positive and inclusive relationships. This awareness fosters a sense of community and interconnectedness. It also contributes to a more supportive environment. The key components of social awareness are empathy, perspective-taking, showing concern for others, expressing gratitude, understanding diverse social norms, and considering various cultural backgrounds.
- Relationship Skills:Building and maintaining healthy relationships is central to every person’s success. SEL emphasizes developing relationship skills, including effective communication, active listening, and collaboration. Students with solid relationship skills can navigate conflicts, work cooperatively with others, and contribute positively to group dynamics.
- Responsible Decision-Making: The final core competency of SEL is responsible decision-making, which involves making informed and ethical choices by considering the well-being of oneself and others. Individuals with good decision-making skills weigh the consequences of their actions, exhibit sound judgment, and act in alignment with their values. This is crucial in preparing children to face the complexities of the real world, empowering them to make choices that contribute to their success and the well-being of their communities.
Integrating Social-Emotional Learning into Education

Photo by Kenny Eliason on Unsplash
SEL is not a standalone practice but should be integrated into all aspects of education. It can be woven into classroom activities, discussions, and extracurricular programs. By creating a culture that values emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills, educators can nurture an environment conducive to both academic and personal success.
Developmentally Appropriate Practices
Recognizing that individuals develop at different rates, SEL incorporates developmentally appropriate practices. It is adaptable to various age groups and lived experiences, ensuring that the content and activities resonate with all students. Effective SEL has to be relevant to students’ past and current classroom experiences.
Inclusivity and Equity
SEL supports all individuals, regardless of background. Effective SEL programs promote inclusivity, equity, and cultural responsiveness, acknowledging and fostering a sense of social responsibility and civic engagement. In addition, they aim to create a supportive and positive school climate where students feel safe, valued, and included. Students are intentionally taught to develop empathy, compassion, a sense of justice, and the skills to work collaboratively and resolve conflicts peacefully.
Continuous Learning and Growth
SEL is not a one-time lesson but an ongoing process. And it doesn’t happen in isolation. At times, educators must explicitly teach a SEL concept or skill. At other times, educators act as facilitators to support students as they practice SEL skills. For example, a morning meeting or a homeroom period may be the perfect opportunity to teach a specific SEL skill, whereas, later in the day, as students are working in groups on a project, the educator can check in with groups and students individuals to support their SEL skills practice during that time. Workaround SEL helps to establish a growth mindset, where individuals recognize that personal development is a lifelong journey. Continuous learning, self-reflection, and adaptation to new challenges are integral aspects of SEL. By fostering SEL skills, individuals are better equipped to navigate the complexities of life and develop resilience in the face of adversity. It benefits personal well-being and contributes to a positive and inclusive community and society. Furthermore, integrating SEL into educational curricula can have a lasting impact on students’ academic achievement and social and emotional growth. Research has shown that SEL programs can lead to improved attitudes toward school, increased academic motivation, and higher social and emotional competence levels. Years after students participated in SEL, their academic performance was an average of 13 percentile points higher than students who didn’t participate.
